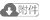2. 页岩气评价与开采四川省重点实验室, 成都 610021
2. Key Laboratory of Gas Evaluation and Exploitation of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610021, China
1964年威远震旦系气藏的发现揭开了四川盆地灯影组勘探的序幕,此后四十余年中,川中古隆起震旦系一直处于被探索、寻求突破的阶段。2011年GS1井灯影组获102.15×104m3/d高产工业气流,勘探取得了重大突破[1],揭开了川中古隆起震旦系大气田勘探的序幕。高石梯—磨溪地区(以下简称高磨地区)位于现今川中古隆起高部位,其以北地区(安岳以北至旺苍地区)为一向北倾覆的单斜构造,简称北斜坡。川中古隆起在震旦纪—早古生代处于发育阶段,受区域沉积和桐湾期多幕次岩溶共同作用[2],形成了灯二段普遍分布的优良储层。高磨地区与北斜坡地区具有相似的构造-沉积背景[3-5],同时灯影组岩性非均质性较强,低能带沉积的岩性较致密,因此现今北斜坡地区灯影组虽然构造位置较低,但依然可能发育岩性油气藏。风险探井PT1井近期在北斜坡灯影组二段(以下简称灯二段)测试获气121.98×104m3/d,预探井ZJ2井在灯二段测试获得3.36×104m3/d工业气流,证实了川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段存在岩性圈闭气藏,具备良好的勘探潜力[6]。以往研究更多关注灯影组四段(以下简称灯四段),灯四段是目前勘探的主要目的层段[7],不仅发现了台缘带富集天然气,而且证实了台内也具有良好的成藏条件[8-9]。随着高磨地区勘探进入中后期,亟需寻找勘探接替领域。灯二段勘探和研究程度较低,以往研究主要聚焦于高磨地区灯二段含油气地质条件以及灯二段沉积期德阳—安岳裂陷槽成因[10-11]。北斜坡灯二段埋藏较深,勘探难度大,灯二段烃源来源不明确、储集条件是否优良、岩性气藏能否成藏以及勘探潜力如何等问题皆不明确。鉴于此,结合新钻探井资料,对川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段开展岩心观察、薄片鉴定、烃源对比、地震相刻画等综合研究,并进一步分析其成藏特征,进行勘探潜力评价,以期为深化该区灯二段天然气成藏认识和后续勘探部署提供参考。
1 地质概况川中古隆起发现于20世纪70年代,自西南部雅安向南充地区依次剥蚀至震旦系—志留系,按照志留系剥蚀区计算,古隆起面积达6.25×104km2[12](图 1a)。上扬子地区在经历了桐湾期两幕次运动后,形成了灯二段和灯四段顶部2个区域性不整合面,在此背景下资阳及西部地区已剥蚀至灯二段,灯四段在盆地内大部分区域不同程度残存[13-15]。四川盆地灯影组厚度为200~1 250 m,岩性主要为富藻白云岩、砂屑云岩、细晶云岩、粉晶白云岩,自下而上分为灯一段至灯四段。其中,灯一段厚度为0~100 m,以泥晶白云岩为主,夹含藻白云岩,俗称“贫藻段”;灯二段又称“富藻段”,厚度为400~ 600 m,岩性主要为富藻白云岩和颗粒白云岩;灯三段为陆棚相沉积,岩性主要为砂岩、泥岩及泥质白云岩,称“碎屑岩段”;灯四段厚度为180~320 m,主要发育泥粉晶云岩和纹层状云岩,以含硅质白云岩为特征(图 1b)。
|
下载原图 图 1 四川盆地川中古隆起二叠纪沉积前形态(a)及震旦系灯影组岩性地层综合柱状图(b) Fig. 1 Pre-sedimentary morphology(a)and stratigraphic column of Sinian Dengying Formation(b)in Sichuan Basin |
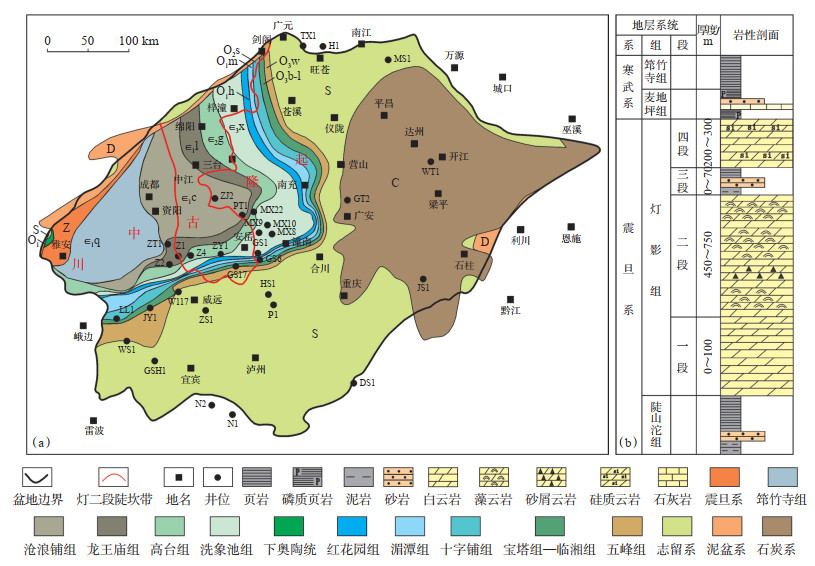
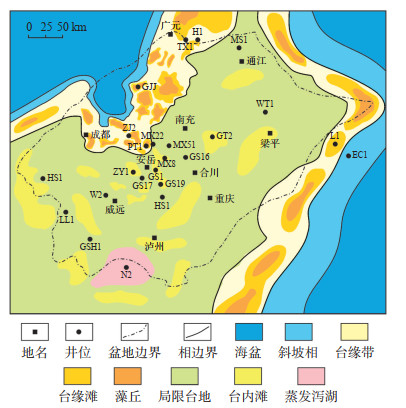
晚震旦世四川盆地灯影组为区域拉张背景下的碳酸盐台地沉积环境[16],灯二段沉积期盆地东南缘、东北缘及西北缘均为被动大陆边缘,西北缘松潘—甘孜海向南伸入到扬子克拉通内部,发育德阳—安岳裂陷槽[17]。灯二段沉积期四川盆地以局限台地沉积为主,长宁地区见巨厚的岩盐、芒硝沉积,为蒸发台地环境。沿德阳—安岳裂陷槽边缘以及被动大陆边缘发育台缘丘滩带(图 2)。川中古隆起北斜坡发育局限台地相和台地边缘相,台缘宽35~ 100 km,台缘藻丘相和颗粒滩相较发育,其中颗粒滩相在PT1井和ZJ2井较为发育。PT1井灯二段底部主要为砂屑云岩,滩相特征明显;中部藻云岩发育,局部见凝块云岩,为藻丘相;顶部岩性以凝块云岩和砂屑云岩为主,夹少量藻云岩和粉晶云岩,滩相特征明显,为台缘颗粒滩相(图 3)。ZJ2井灯二段未钻穿,实钻370 m,岩性与PT1井灯二段也具有相似特征,底部和顶部岩性以凝块云岩和砂屑云岩为主,滩相特征明显,中部岩性以藻云岩夹少量凝块云岩为主,藻丘相发育。
|
下载原图 图 2 四川盆地震旦系灯二段沉积相 Fig. 2 Sedimentary facies of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin |
|
下载原图 图 3 川中古隆起北斜坡PT1井震旦系灯二段综合柱状图 Fig. 3 Comprehensive column of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation of well PT1 in the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段储层岩性主要为凝块云岩、砂屑云岩以及少量粉晶云岩,储集空间主要为溶洞(图 4a)、溶孔和溶缝[6]。其中溶孔主要为粒间溶孔(图 4b—4e)、粒内溶孔(图 4c)和晶间溶孔(图 4f)。岩心上溶蚀孔洞发育,见大量顺层溶蚀孔洞,可能是颗粒滩在桐湾运动抬升至地表环境下受顺层溶蚀而形成,还可见针状溶孔、大溶洞及高角度缝[18-19]。
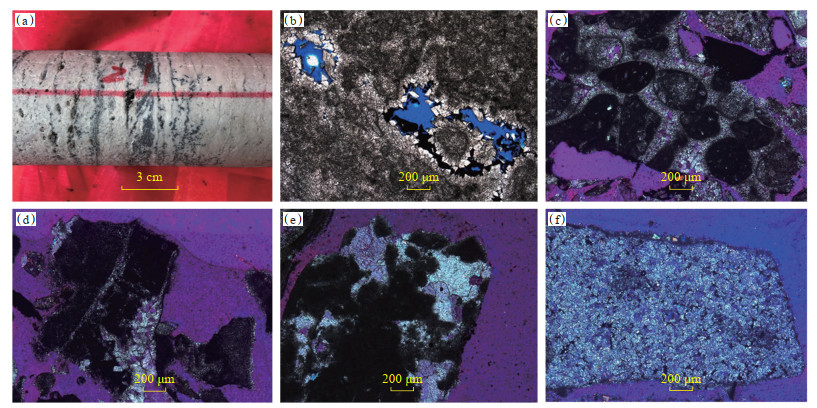
|
下载原图 图 4 川中古隆起北斜坡震旦系灯二段储层典型岩石学特征 (a)砂屑云岩,部分溶蚀孔洞见沥青,ZJ2井,6 556.07~6 556.18 m;(b)砂屑云岩,粒间溶孔部分被沥青充填,ZJ2井,6 554.57 m,单偏光;(c)砂屑云岩,粒间溶孔,粒内溶孔,PT1井,5 720.00 m,加石膏试板;(d)凝块云岩,粒间溶孔,PT1井,5 840.00 m,加石膏试板;(e)凝块云岩,粒间溶孔,ZJ2井,6 763.00 m,加石膏试板;(f)粉晶云岩,部分晶间溶孔充填沥青,ZJ2井,6 687.00 m,加石膏试板。 Fig. 4 Typical petrological characteristics of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段储层厚度为119.8~ 233.3 m,平均为176.6 m,平均储地比为34.6%,整体上具有低孔低渗特征,局部孔隙度较高。岩心孔隙度为2.0%~10.7%,平均为4.4%;岩心(柱塞样) 平均渗透率为3.6 mD。高磨地区灯二段储层总体要薄一些,厚度为17.4~375.1 m,平均厚度为89.7 m,平均孔隙度为3.4%,平均储地比为32.4% (表 1)。通过对比发现北斜坡灯二段储集条件总体上较高磨地区更加优良,这可能是由于台缘滩储集条件整体优于台内滩造成的。
|
|
下载CSV 表 1 川中古隆起高磨地区与北斜坡震旦系灯二段储层特征对比 Table 1 Reservoir characteristics comparison of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaomo area and the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
四川盆地震旦系—寒武系烃源岩发育,包括陡山沱组、筇竹寺组及麦地坪组泥岩等多套有机质丰度较高的烃源岩[20-22]。北斜坡多口实钻探井已证实在古隆起北斜坡广覆式发育筇竹寺组、麦地坪组和陡山沱组等多套烃源岩,其中尤以筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度大、有机碳含量高。位于北斜坡的PT1井筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度为285 m,实测有机碳质量分数为0.37%~6.56%,平均为2.11%,其天然气δ13C1值为-34.0‰~-33.6‰,δ13C2值为-29.3‰~-28.9‰(表 2)。PT1井天然气的δ13C2值比筇竹寺组泥页岩干酪根的δ13C2值重,说明PT1井天然气不仅仅来自筇竹寺组烃源岩,其甲、乙烷碳同位素与高磨地区震旦系天然气藏处于同一个区间范围内,与威远、资阳灯影组气藏差异比较大(图 5),表明北斜坡PT1井灯二段天然气来源与高磨地区灯影组气藏相似,即气源为深部震旦系烃源岩与筇竹寺组烃源岩共同供气[19]。位于德阳—安岳裂陷槽内的ZJ2井筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度为506 m,实测有机碳质量分数为1.30%~2.55%,平均为2.03%,其天然气δ13C1值为-35.1‰~-34.7‰,δ13C2值为-33.2‰~-27.3‰。其乙烷碳同位素分布范围较广,部分与筇竹寺组干酪根的δ13C2值接近,部分与灯影组碳酸盐岩δ13C2值接近,表明ZJ2井灯二段天然气来源主要为筇竹寺组烃源岩和深部震旦系烃源岩共同供气。
|
|
下载CSV 表 2 川中古隆起震旦系灯二段同位素分布 Table 2 Isotope distribution of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
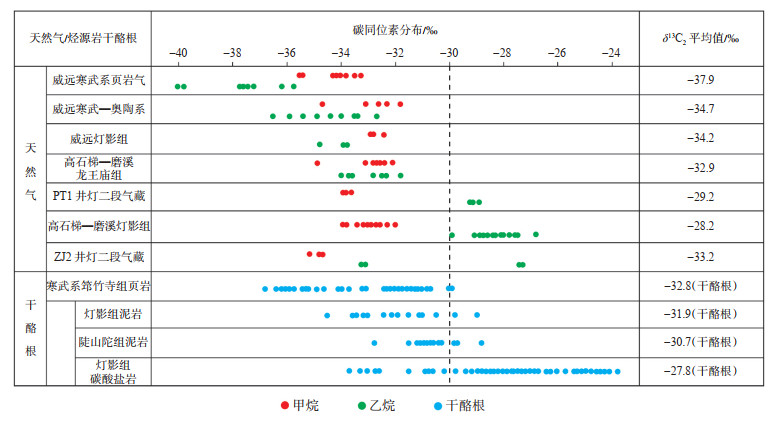
|
下载原图 图 5 四川盆地震旦系—下古生界天然气与烃源岩干酪根碳同位素分布 Fig. 5 Distribution of kerogen carbon isotopes of natural gas and source rocks of Sinian-Lower Paleozoic in Sichuan Basin |
结合钻井、地震资料,刻画出高磨地区—北斜坡筇竹寺组烃源岩展布,其整体呈现出沿德阳—安岳裂陷槽分布,在裂陷槽形成了生烃中心[21]。北斜坡灯二段不仅上覆烃源条件良好,还紧邻裂陷槽生烃中心,筇竹寺烃源岩厚度为200~600 m,为灯二段成藏提供了充足的烃源(图 6)。
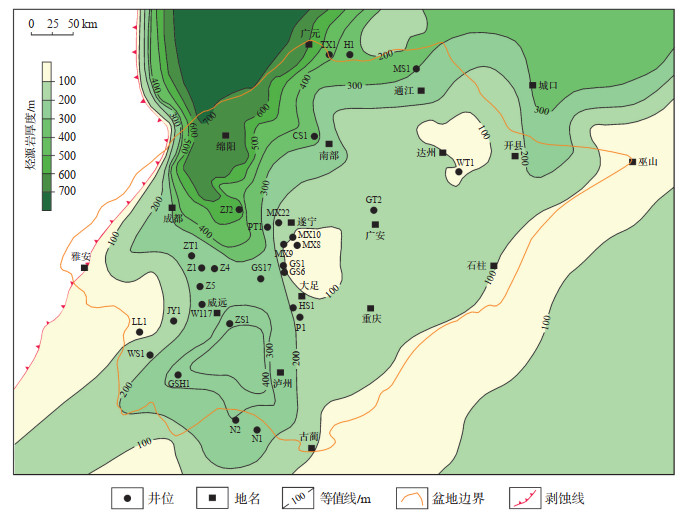
|
下载原图 图 6 川中古隆起北斜坡下寒武统筇竹寺组烃源岩厚度 Fig. 6 Thickness of source rocks of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
川中古隆起北斜坡筇竹寺组、麦地坪组烃源岩条件良好, 灯二段丘滩体储层叠置连片, 分布面积广, 筇竹寺组和麦地坪组烃源岩从侧向及上方包裹丘滩体, 同时具备"上生下储"和"旁生侧储"2种良好的源储配置关系[23](图 7a)。灯二段顶面桐湾运动一期形成的区域性不整合面和大量断层系统有效沟通了烃源岩和储集层, 为古隆起及其围斜区油气成藏提供了良好的运移通道[21, 24]。高磨地区灯二段台内丘滩体储层与筇竹寺组烃源岩呈上下叠置关系, 主要构成"上生下储"的源储配置关系(图 7b)。总体而言, 从烃源岩厚度和质量, 以及源储配置关系来看, 北斜坡相对于古隆起高部位的高磨地区成藏条件更为优越。
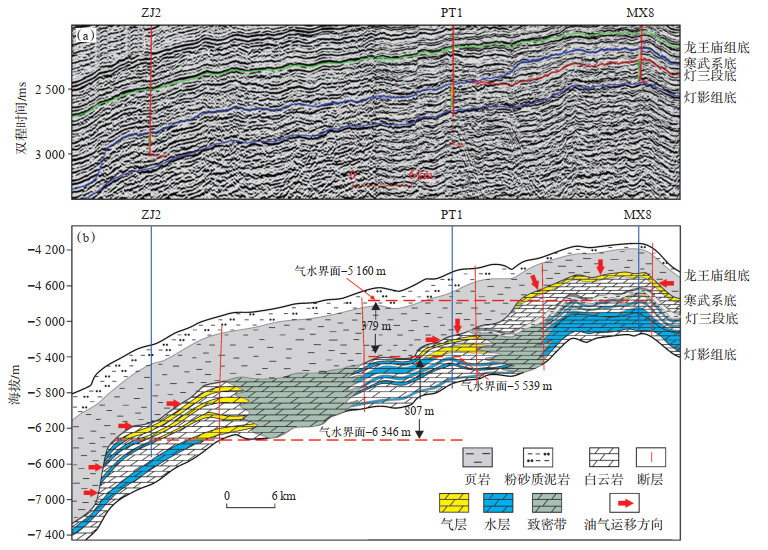
|
下载原图 图 7 川中古隆起北斜坡—高磨地区连井地震剖面(a)及气藏剖面(b) Fig. 7 Well-tie seismic section(a)and gas reservoir profile(b)in Gaomo area and the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
高磨地区灯二段为一具有统一气水界面(-5 160 m) 的底水构造圈闭气藏。PT1井区的构造圈闭面积为90 km2, 构造幅度为200 m, 测井解释气水界面为-5 539 m, 气水界面之上构造-岩性圈闭面积为145 km2。PT1井气柱高度达到230 m, 超过构造幅度, 为斜坡背景下的大型构造-岩性复合圈闭。PT1井区灯二段气藏气水界面比高磨地区灯二段气水界面低379 m, 表明2个地区存在不同的气水系统[6]。ZJ2井区灯二段气藏为岩性圈闭气藏, 不受局部构造控制, 测井解释气水界面为-6 346 m, 气柱高度为214 m。ZJ2井区灯二段岩性气藏气水界面比PT1井区灯二段气水界面低807 m, 表明这2个气藏具有相对独立的气水系统。地震属性及地震相表明, ZJ2井、PT1井、MX8井均位于丘滩相, 地层厚度明显增大, 地震相呈丘状杂乱反射、断续滩相特征, 而ZJ2井和PT1井上倾方向具有相似特点, 都存在大型断裂且地震剖面上显示平行连续反射。具平行反射特征地震相的岩性致密带推测为滩间海沉积的水体能量较弱的泥晶云岩、泥质云岩, 上倾方向大型断裂以及岩性致密带封堵是ZJ2井区和PT1井区油气成藏及形成不同气水系统的关键。
3.4 有利勘探区带及勘探潜力川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段构造-岩性圈闭气藏、岩性圈闭气藏的形成与其烃源条件优良、储层发育、源储配置关系良好、上倾方向大型断裂以及岩性致密带封堵等优越的成藏条件密不可分。利用现有地震资料,对川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段内岩性圈闭分布情况进行了刻画。在台缘带刻画出12个大型丘滩体(图 8),累计面积7 202.3 km2,台内刻画出5个大型独立滩体,面积合计3 294.6 km2。按照PT1井灯二段储量丰度为10×108 m3/km2计算的台缘圈闭天然气资源量为0.72×1012 m3,台内圈闭天然气资源量为0.33×1012m3,台缘、台内圈闭天然气资源量合计1.05×1012m3,勘探潜力巨大,是未来川中古隆起区寻求规模优质储量的重要接替领域。
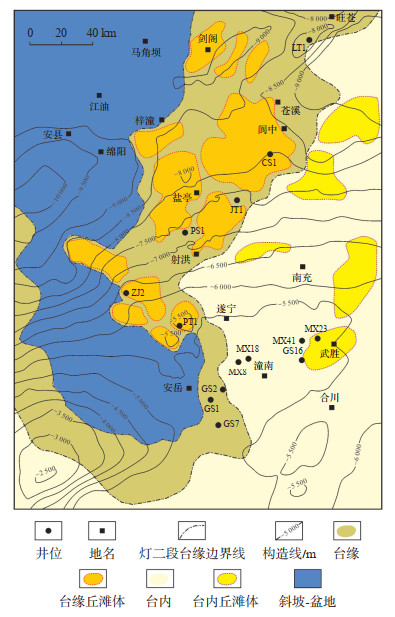
|
下载原图 图 8 川中古隆起北斜坡震旦系灯二段藻丘、滩有利区预测 Fig. 8 Prediction of favorable areas for algal mound and shoals of the second member of Sinian Dengying Formation in the north slope of central Sichuan paleo-uplift |
(1) 川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段沉积期主要发育局限台地相和台地边缘相,台缘藻丘相和颗粒滩相均较发育。灯二段储层厚度平均为176.6 m,平均储地比为34.6%,岩心平均孔隙度为4.4%;平均渗透率为3.6 mD,整体上具有低孔低渗特征。研究区储集条件整体上优于高磨地区。
(2) 川中古隆起北斜坡成藏条件优越,发育震旦系陡山沱组、寒武系筇竹寺组、麦地坪组泥页岩等多套烃源岩,烃源岩厚度大、有机碳含量高。气-源碳同位素表明北斜坡灯二段天然气主要来源于筇竹寺组烃源岩和深部震旦系烃源岩,源储配置条件具备“上生下储”和“旁生侧储”2种类型。油气藏类型为构造-岩性气藏和岩性气藏,上倾方向的大型断裂以及岩性致密带的有效封堵是油气成藏及形成不同气水系统的关键。
(3) 川中古隆起北斜坡灯二段具备形成大气田的地质条件,预测的台缘、台内圈闭的总资源量约为1.05×1012m3,勘探潜力巨大,北斜坡是未来川中古隆起区大气田发育的潜在区域。
| [1] |
李国玉, 陈启林, 白云来, 等. 再论海相沉积是中国石油工业未来的希望. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(6): 1-7. LI Guoyu, CHEN Qilin, BAI Yunlai, et al. Marine sediment: The future expectation of China's petroleum industry. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(6): 1-7. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.06.001 |
| [2] |
毛治国, 崔景伟, 綦宗金, 等. 风化壳储层分类、特征及油气勘探方向. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(2): 12-22. MAO Zhiguo, CUI Jingwei, QI Zongjin, et al. Classification, characteristics and petroleum exploration of weathering crust reservoir. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(2): 12-22. |
| [3] |
徐春春, 沈平, 杨跃明, 等. 乐山-龙女寺古隆起震旦系-下寒武统龙王庙组天然气成藏条件与富集规律. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(3): 1-7. XU Chunchun, SHEN Ping, YANG Yueming, et al. Accumulation conditions and enrichment patterns of natural gas in the Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Fm reservoirs of the Leshan-Longnüsi Paleohigh, Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 1-7. DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.03.001 |
| [4] |
许海龙, 魏国齐, 贾承造, 等. 乐山-龙女寺古隆起构造演化及对震旦系成藏的控制. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(4): 406-416. XU Hailong, WEI Guoqi, JIA Chengzao, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Leshan-Longnüsi paleo-uplift and its control on gas accumulation in the Sinian strata, Sichuan Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(4): 406-416. |
| [5] |
罗冰, 周刚, 罗文军, 等. 川中古隆起下古生界-震旦系勘探发现与天然气富集规律. 中国石油勘探, 2015, 20(2): 18-29. LUO Bing, ZHOU Gang, LUO Wenjun, et al. Discovery from exploration of Lower Paleozoic-Sinian system in central Sichuan palaeo-uplift and its natural gas abundance law. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015, 20(2): 18-29. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2015.02.003 |
| [6] |
赵路子, 汪泽成, 杨雨, 等. 四川盆地蓬探1井灯影组灯二段油气勘探重大发现及意义. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(3): 1-12. ZHAO Luzi, WANG Zecheng, YANG Yu, et al. Important discovery in the second member of Dengying Formation in well Pengtan 1 and its significance, Sichuan Basin. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(3): 1-12. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.001 |
| [7] |
戴晓峰, 谢占安, 杜本强, 等. 高石梯-磨溪地区灯影组多次波控制因素及预测方法. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(4): 89-97. DAI Xiaofeng, XIE Zhan'an, DU Benqiang, et al. Controlling factors and prediction methods of multiples of Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(4): 89-97. |
| [8] |
田兴旺, 彭瀚霖, 王云龙, 等. 川中安岳气田震旦系灯影组四段台缘-台内区储层差异及控制因素. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(9): 1225-1238. TIAN Xingwang, PENG Hanlin, WANG Yunlong, et al. Analysis of reservoir difference and controlling factors between the platform margin and the inner area of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Anyue gas field, central Sichuan. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(9): 1225-1238. |
| [9] |
杨威, 魏国齐, 谢武仁, 等. 四川盆地绵竹-长宁克拉通内裂陷东侧震旦系灯影组四段台缘丘滩体成藏特征与勘探前景. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1174-1184. YANG Wei, WEI Guoqi, XIE Wuren, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration prospect of mound-shoal complexes on the platform margin of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in the east of Mianzhu-Changning intracratonic rift, Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1174-1184. |
| [10] |
王良军. 川北地区灯影组四段优质储层特征及控制因素. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(2): 35-45. WANG Liangjun. Characteristics and controlling factors of highquality reservoirs of the fourth member of Dengying Formation in northern Sichuan Basin. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(2): 35-45. |
| [11] |
文龙, 王文之, 李林娟, 等. 川西南部灯影组展布特征新认识及油气地质勘探意义. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(3): 56-65. WEN Long, WANG Wenzhi, LI Linjuan, et al. New understandings of distribution characteristics of Sinian Dengying Formation in southwestern Sichuan Basin and its significance of oil and gas geological exploration. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(3): 56-65. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.006 |
| [12] |
罗冰, 杨跃明, 罗文军, 等. 川中古隆起灯影组储层发育控制因素及展布. 石油学报, 2015, 36(4): 416-426. LUO Bing, YANG Yueming, LUO Wenjun, et al. Controlling factors and distribution of reservoir development in Dengying Formation of paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(4): 416-426. |
| [13] |
李启桂, 李克胜, 周卓铸, 等. 四川盆地桐湾不整合面古地貌特征与岩溶分布预测. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(4): 516-521. LI Qigui, LI Kesheng, ZHOU Zhuozhu, et al. Palaeogeomor-phology and karst distribution of Tongwan unconformity in Sichuan Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(4): 516-521. |
| [14] |
杨雨, 黄先平, 张健, 等. 四川盆地寒武系沉积前震旦系顶界岩溶地貌特征及其地质意义. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(4): 38-43. YANG Yu, HUANG Xianping, ZHANG Jian, et al. Features and geologic significances of the top Sinian karst landform before the Cambrian deposition in the Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(4): 38-43. |
| [15] |
汪泽成, 姜华, 王铜山, 等. 四川盆地桐湾期古地貌特征及成藏意义. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 305-312. WANG Zecheng, JIANG Hua, WANG Tongshan, et al. Paleo-geomorphology formed during Tongwan tectonization in Sichuan Basin and its significance for hydrocarbon accumulation. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 305-312. |
| [16] |
刘树根, 孙玮, 李智武, 等. 四川叠合盆地海相碳酸盐岩油气分布特征及其构造主控因素. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(5): 1-17. LIU Shugen, SUN Wei, LI Zhiwu, et al. Distribution characteristics of marine carbonate reservoirs and their tectonic controlling factors across the Sichuan superimposed basin. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2016, 28(5): 1-17. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2016.05.001 |
| [17] |
文龙, 罗冰, 钟原, 等. 四川盆地灯影期沉积特征及槽-台体系成因模式. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 48(5): 513-524. WEN Long, LUO Bing, ZHONG Yuan, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and genetic model of trough-platform system during the Dengying period in Sichuan Basin, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2021, 48(5): 513-524. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2021.05.01 |
| [18] |
王文之, 杨跃明, 张玺华, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组储层特征及成因. 东北石油大学学报, 2016, 40(2): 1-10. WANG Wenzhi, YANG Yueming, ZHANG Xihua, et al. Reservoir characteristics and genesis of the Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2016, 40(2): 1-10. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.02.001 |
| [19] |
徐哲航, 兰才俊, 马肖琳, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组丘滩体储层沉积模式与物性特征. 地球科学, 2020, 45(4): 1281-1294. XU Zhehang, LAN Caijun, MA Xiaolin, et al. Sedimentary models and physical properties of mound-shoal complex reservoirs in Sinian Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin. Earth Science, 2020, 45(4): 1281-1294. |
| [20] |
张玺华, 罗文军, 文龙, 等. 四川盆地寒武纪龙王庙组沉积相演化及石油地质意义. 断块油气田, 2018, 25(4): 419-425. ZHANG Xihua, LUO Wenjun, WEN Long, et al. Sedimentary facies evolution characteristics and petroleum geological significance of Cambrian Group in Sichuan Basin. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2018, 25(4): 419-425. |
| [21] |
杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰, 等. 四川盆地乐山一龙女寺古隆起震旦系天然气成藏特征. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(2): 1-10. YANG Yueming, WEN Long, LUO Bing, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation of Sinian natural gas reservoirs, Leshan-Longnüsi paleohigh, Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(2): 1-10. |
| [22] |
赵建华, 金之均, 林畅松, 等. 上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩沉积环境. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(4): 701-715. ZHAO Jianhua, JIN Zhijun, LIN Changsong, et al. Sedimentary environment of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation shale in the Upper Yangtze region. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(4): 701-715. |
| [23] |
徐春春, 沈平, 杨跃明, 等. 四川盆地川中古隆起震旦系-下古生界天然气勘探新认识及勘探潜力. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(7): 1-9. XU Chunchun, SHEN Ping, YANG Yueming, et al. New understandings and potential of Sinian-Lower Paleozoic natural gas exploration in the central Sichuan paleo-uplift of the Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(7): 1-9. |
| [24] |
杨光, 李国辉, 李楠, 等. 四川盆地多层系油气成藏特征与富集规律. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(11): 1-11. YANG Guang, LI Guohui, LI Nan, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and enrichment laws of multi-layered reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(11): 1-11. |
 2022, Vol. 34
2022, Vol. 34