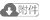2. 中国石油化工集团公司 碳酸盐岩缝洞型油藏提高采收率重点实验室, 乌鲁木齐 830011;
3. 油气钻采工程湖北省重点实验室, 武汉 430100;
4. 长江大学 油气钻完井技术国家工程研究中心, 武汉 430100;
5. 中海油研究总院, 北京 100028
2. Key Laboratory of Enhanced Oil Recovery in Carbonate Fractured-Vuggy Reservoirs, Sinopec, Urumqi 830011, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Drilling and Production Engineering for Oil and Gas, Hubei Province, Wuhan 430100, China;
4. National Engineering Research Center for Oil & Gas Drilling and Completion Technology, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430100, China;
5. CNOOC Research Institute Co., Ltd., Beijing 100028, China
缝洞型油藏分布广泛,井间单套结构属于典型的缝洞型油藏,该类油藏的基质岩性致密,主要储集空间为裂缝和溶蚀孔洞[1-2]。在开发过程中,采油速度快,油层压力下降,导致地层供液不足,为了维持较高的采收率,往往需通过注水补充地层能量[3-4],但由于储集体内部及储集体之间连通关系复杂,油藏非均质性强[5-7],注水开发易发生水窜,横向上表现为舌进,纵向上表现为单层突进,致使油井暴性水淹,影响整体开采效果[8-9]。实践已经证明了调剖堵水是改善水驱效果的有效措施[10-12],目前常用的堵水调流剂有水泥型、凝胶型、冻胶型、树脂型和橡胶颗粒。水泥型调流剂堵水成本低、凝结快、耐温抗盐性好,在高渗油藏应用较为广泛,但存在遇水易稀释、堵水有效期短的问题[13-15];凝胶型调流剂封堵强度高且适用于非选择性堵水,但在高温油藏条件下固化时间不易控制,容易造成调流剂还未到达封堵目的层就在井筒内固化的现象[16-18];冻胶型调流剂由高分子聚合物溶液在交联剂作用下失去流动性而形成网状结构,具有良好的热稳定性和耐冲刷性能,但受到井筒内Ph值和地层矿化度的影响易脱水[19-21];树脂型调流剂抗压强度大,对裂缝、孔隙具有良好的封堵效果,但成本高、有毒性且不适用于高渗油藏;橡胶颗粒调流剂是由废旧轮胎经过切块、粉碎等工艺加工而成,价格低廉、来源广泛、绿色环保,可在地层条件下通过架桥-堆积-运移等方式形成暂堵带,迫使后续注入水转向中、低渗透层,从而提高了井间单套缝洞型油藏的波及系数,在地层条件下注入性好、封堵强度大,适用于缝洞型油藏堵水。然而,由于缝洞型油藏的地质特征与砂岩油藏差异大,无法精细刻画储集体内部结构、相对位置及连通关系,堵水实施难度大。
以塔河油田典型生产工区为模型基础,设计可视化物理模型,进行井间单套缝洞型油藏的物理模拟实验,通过实验分析水驱机理,观察不同封堵位置、不同注水速度以及不同的橡胶颗粒用量和粒径的情况下,油水的流动规律及剩余油分布情况,以期优化堵水施工技术参数、提高采收率。
1 实验设计 1.1 实验模型以塔河油田某一生产区域的三维地震响应和生产动态确定的储集体为模型基础,将该区域的不同形态、尺寸的缝洞按比例缩小,制作井间单套缝洞型油藏模型。模型主要由横向顶部通道,横向中部通道,横向底部通道,注水井和采油井构成(图 1)。模型便于拆卸,可以避免因调流后橡胶颗粒排出不完全而影响下一组实验。
|
下载原图 图 1 塔河油田典型井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验模型 Fig. 1 Simulation experimental model of rubber particle profile control and water plugging in a typical inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir in Tahe Oilfield |
根据相似准则设计实验参数和物理模型(表 1),以保证物理模拟实验与油田实际情况相符。设计模型长40 cm,宽30 cm,厚5 cm,裂缝开度为4~20 mm,溶洞直径为2~4 cm,井筒宽度为10 mm,模型缝洞体积为175 mL。此外,模型耐温80 ℃,耐压2 MPa。
|
|
下载CSV 表 1 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验相似参数设计 Table 1 Design of similar parameters in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
实验用水是根据现场实际注入水的离子组成配制的模拟地层水(表 2),实验用油为与实际地层原油黏度相同的模拟油。为了提高可视化效果,分别在模拟油和模拟水中加入苏丹Ⅱ(红色)和亚甲基蓝(浓度低时呈灰色,浓度高时为蓝色)。模拟调剖堵水采用的橡胶颗粒由废旧的轮胎加工而成,根据1/3~1/7架桥理论和油田现有的橡胶颗粒筛选出符合要求的颗粒粒径(小于1 mm和2~4 mm),同时选定混合颗粒中粒径小于1 mm的颗粒和粒径为2~4 mm的颗粒各占50%。
|
|
下载CSV 表 2 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验地层水离子组成 Table 2 Formation water ion composition in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
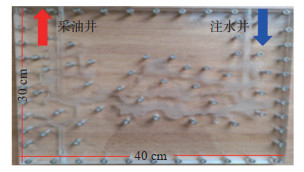
根据矿场实施过程设计实验流程(图 2)。①连接实验装置并检测气密性。②将井间单套缝洞型油藏模型竖起,模拟成藏过程,对模型抽真空、饱和水,再用油驱水。③注水驱油。在温度25 ℃,常压情况下,以10 mL/min的注水速度进行水驱,直到采油井产出液体含水率达到98%,停止实验。④橡胶颗粒调剖堵水测试。通过预置不同封堵位置、颗粒的用量和粒径以及注水速度,继续进行水驱油,直到采油井产出液体含水率再次达到98%,停止实验。实验期间记录油水分布情况、驱替压力与采出程度随注水时间的变化关系。
|
下载原图 图 2 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验流程 Fig. 2 Simulation experiment process of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
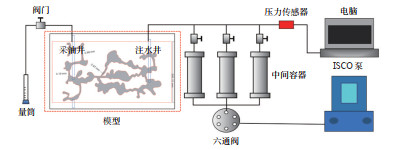
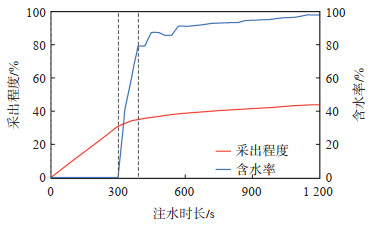
设置温度为25 ℃,常压,注水速度为10 mL/min,注水驱替至采油井含水率达到98%。实验结果显示:①由于重力分异作用,注入水优先驱替油藏横向底部通道和横向中部通道的原油,随着注水时间的推移,优势通道形成,最终剩余油主要以阁楼油(由于油水密度差的影响,导致注入水无法波及而未能进行油水置换的剩余油)和少量绕流油(由于油水黏度差和密度差的影响,导致注入水可以波及但无法携带走的剩余油)的形式存在。阁楼油主要集中在横向顶部通道,绕流油主要集中在横向中部通道和横向底部通道的高位,油水界面与横向中部通道的高位缝齐平(图 3)。②当注水时长为0~300 s时,采出程度随注水时长增加呈线性增加,几乎不产水,无水采油期采出程度为30.86%;注水时长为300~400 s时,含水率急剧上升至85%,表明油水前缘开始到达采油井,油井已经见水;注水时长超过400 s后,采出程度几乎不变,含水率达到98%,优势通道已经完全形成,最终采出程度为43.83%(图 4)。
|
下载原图 图 3 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中注水驱替前(a)、驱替中(b)和驱替后(c)的油水分布 Fig. 3 Oil-water distribution before(a), during (b) and after (c) water flooding in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
|
下载原图 图 4 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中不同注水时长的采出程度和含水率的变化 Fig. 4 Changes of recovery rate and water content in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles at different water injection times in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
由井间单套缝洞型油藏的水驱规律可知,其优势通道主要为横向底部通道和横向中部通道。设置温度为25 ℃,常压,转注时机含水率为98%,注水速度为10 mL/min,橡胶颗粒用量为0.04 PV,颗粒粒径为2~4 mm,颗粒密度和模拟地层水密度一致,分别封堵横向底部通道、横向中部通道、同时封堵横向底部通道和中部通道,在以上3个不同的封堵状态进行实验并记录实验现象。
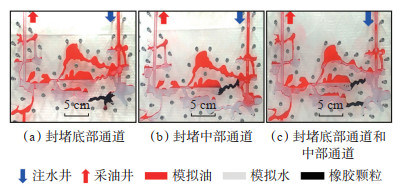
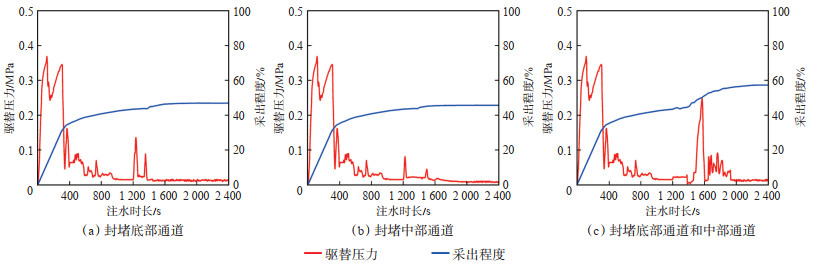
实验结果显示:①封堵横向底部通道时,优势通道变为横向中部通道,该区域部分绕流油被采出,但注入水仍无法达到顶部通道,顶部通道中阁楼油未被启动,调流效果较差(图 5a);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.136 MPa,采出程度为46.92%,提高幅度为3.09%(图 6a)。②封堵横向中部通道时,优势通道变为底部通道,顶部通道阁楼油几乎没有变化,调流效果差(图 5b);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.081 MPa,采出程度为45.67%,提高幅度为1.84%(图 6b)。③当同时封堵横向底部通道和中部通道时,优势通道变为顶部通道,顶部通道阁楼油被采出,提高了波及系数,调流效果好(图 5c);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.248 MPa,采出程度为57.31%,提高幅度为13.48%(图 6c)。
|
下载原图 图 5 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中封堵不同优势通道时驱替后的油水分布 Fig. 5 Oil-water distribution after displacement when plugging different dominant channels in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles at different water injection times in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
|
下载原图 图 6 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中封堵不同优势通道时驱替压力与采出程度的变化 Fig. 6 Changes of displacement pressure and recovery rate when plugging different dominant channels in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
综上所述,同时封堵双优势通道可以极大地增加井间单套缝洞型油藏的波及系数,从而提高了顶层通道的采出程度。因此,同时封堵横向底部通道和横向中部通道驱油效果更好。
2.3 橡胶颗粒参数 2.3.1 用量设置实验温度为25 ℃,常压,转注时机含水率为98%,封堵横向底部通道和中部通道,颗粒粒径为2~4 mm,颗粒密度和模拟地层水密度一致,注水速度为10 mL/min,分别以不同的橡胶颗粒用量0.02 PV,0.04 PV,0.06 PV,进行井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验,观察并记录3次实验结果。
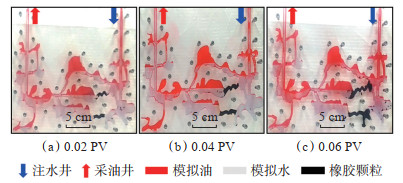
实验结果显示:①当橡胶颗粒用量为0.02 PV时,调流剂的用量较少,封堵段颗粒较为疏松,孔隙体积较大,随着注入水不断挤压,颗粒易发生运移,水体易突破暂堵带从原优势通道到达采油井,导致顶部通道波及系数较低,调流效果较差(图 7a);水驱结束的后驱替压力峰值为0.172 MPa,采出程度为54.82%,提高幅度为10.99%(图 8a)。②当橡胶颗粒用量为0.04 PV时,封堵强度大,封堵段不易坍塌,注水驱替后,注入水从横向顶部通道流动,阁楼油被启动,调流效果好(图 7b);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.248 MPa,采出程度为57.31%,提高幅度为13.48%(图 8b)。③当橡胶颗粒用量为0.06 PV时,虽然封堵强度大,能够有效封堵原优势通道,但剩余油采出程度与用量为0.04 PV相比变化较小(图 7c);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.253 MPa,采出程度为57.61%,提高幅度为13.78%(图 8c)。
|
下载原图 图 7 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中以不同橡胶颗粒用量驱替后的油水分布 Fig. 7 Oil-water distribution after displacement with different rubber particles amount in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |

|
下载原图 图 8 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中不同橡胶颗粒用量对应的驱替压力及采出程度的变化 Fig. 8 Changes of displacement pressure and recovery rate with different rubber particles amount in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
综上所述,橡胶颗粒的用量越大,封堵强度也随之增强,使得后续水体流动方向转向横向顶部通道,造成井周单套缝洞油藏储层的纵向波及系数增加,从而提高了井间单套缝洞型油藏的采出程度。然而,当橡胶颗粒用量为0.06 PV时,提高幅度较小,考虑到油田实际生产成本,橡胶颗粒用量为0.04 PV时更好。
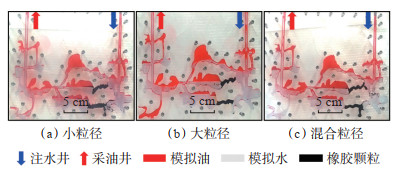
2.3.2 粒径设置实验温度为25 ℃,常压,转注时机含水率为98%,封堵横向底部通道和横向中部通道,橡胶颗粒用量为0.04 PV,颗粒密度和模拟地层水密度一致,注水速度10 mL/min,分别设置3种颗粒粒径,小粒径小于1 mm,大粒径2~4 mm以及混合粒径小于1 mm和2~4 mm的颗粒各一半进行井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验。
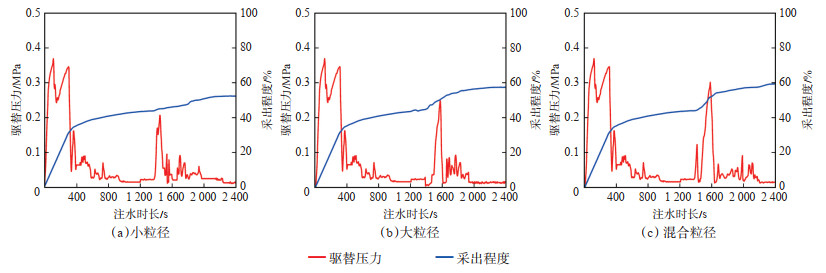
实验结果显示:①当采用粒径为小于1 mm的颗粒调流时,因颗粒粒径较小,易运移,封堵有效期短(图 9a);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.206 MPa,采出程度为52.36%,提高幅度为8.53%(图 10a)。②当采用粒径为2~4 mm的颗粒调流时,颗粒在横向底部通道和横向中部通道具有良好的架桥能力,但由于颗粒间孔隙较大,封堵强度较小,调流效果较差(图 9b);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.248 MPa,采出程度为57.31%,提高幅度为13.48%(图 10b)。③当采用粒径为小于1 mm和2~4 mm的混合颗粒调流时,小粒径橡胶颗粒填充大粒径橡胶颗粒间的孔隙,封堵强度大,调流效果好(图 9c);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值0.301 MPa,采出程度为59.26%,提高幅度为15.43%(图 10c)。
|
下载原图 图 9 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中以不同粒径的橡胶颗粒封堵驱替后的油水分布 Fig. 9 Oil-water distribution after displacement with different rubber particle sizes in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
|
下载原图 图 10 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中以不同粒径的橡胶颗粒封堵后的驱替压力及采出程度变化 Fig. 10 Changes of displacement pressure and recovery rate with different rubber particle sizes in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
综上所述,大粒径橡胶颗粒具有良好的架桥作用,小粒径橡胶颗粒可以起到充填作用,从而提高了封堵强度,导致水体转向,提高了横向顶部通道的采出程度,因此混合粒径调流效果更好。
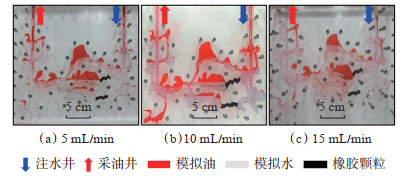
2.4 注水速度设置实验温度为25 ℃,常压,转注时机含水率为98%,封堵横向底部通道和横向中部通道,橡胶颗粒用量为0.04 PV,混合颗粒中粒径小于1 mm和2~4 mm的颗粒各50%,颗粒密度和模拟地层水密度一致,分别以不同的注水速度5 mL/min,10 mL/min,15 mL/min进行实验,并观察结果。
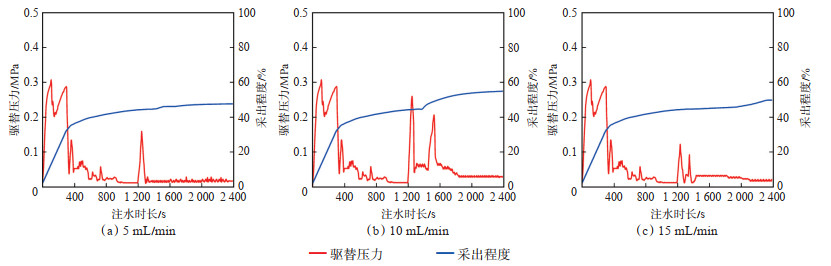
实验结果显示:①注水速度为5 mL/min时,驱替压力小,水体携带原油能力弱,调流效果差(图 11a);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值0.238 MPa,采出程度为55.17%,提高幅度为11.34%(图 12a)。②注水速度为10 mL/min时,流速增大,使洗油效率和纵向波及系数均增大,从而提高了横向顶部通道阁楼油的采出程度(图 11b);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值0.301 MPa,采出程度为59.26%,提高幅度为15.43%(图 12b)。③注水速度为15 mL/min时,封堵压力增大,当垂向压力梯度高于重力时,注入水克服重力向上流动,可很好地波及高部位溶洞内剩余油,调流效果好(图 11c);水驱结束后的驱替压力峰值为0.321 MPa,采出程度为62.28%,提高幅度为18.45%(图 12c)。
|
下载原图 图 11 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中不同注水速度驱替后的油水分布 Fig. 11 Oil-water distribution after displacement with different injection rate in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
|
下载原图 图 12 井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中不同注水速度对应的驱替压力及采出程度变化 Fig. 12 Changes of displacement pressure and recovery rate with different injection rate in the simulation experiment of profile control and water plugging of rubber particles in inter-well single fractured-vuggy reservoir |
综上所述,注水速度越大,水体携带原油能力越强,洗油效率越高,同时重力分异作用越不明显,注入水可到达横向顶部通道,提高了纵向波及系数,所以注水速度为15 mL/min驱替效果更好。
2.5 随机调流分析设计实验温度为25 ℃,常压,转注时机含水率为98%,介质为模拟地层水,封堵横向底部通道和横向中部通道,橡胶颗粒为混合粒径(粒径小于1 mm和粒径为2~4 mm的颗粒各一半),以15 mL/min注入水和不同密度、用量的橡胶颗粒,密度比模拟地层水小为低密度颗粒,密度和模拟地层水一样为等密度颗粒,密度比模拟地层水大为高密度颗粒。
实验结果显示:①随水注入低密度橡胶颗粒时,颗粒的密度介于模拟地层水和原油之间,由于重力分异作用,颗粒运移到横向中部通道,但横向底部通道仍为优势通道,调流效果差;水驱结束后驱替压力峰值为0.192 MPa,采出程度为46.91%,提高幅度为3.08%。②随水注入等密度橡胶颗粒时,由于颗粒密度与注入水接近,注入水可携带颗粒运移到横向底部通道和中部通道,具有良好的封堵效果,调流效果更好;水驱结束后驱替压力峰值为0.312 MPa,采出程度为54.22%,提高幅度为10.39%。③随水注入高密度橡胶颗粒时,颗粒密度大于模拟地层水,由于重力分异作用,大多数颗粒运移到横向底部通道,少数颗粒运移到横向中部通道,调流效果较差;水驱结束后驱替压力峰值为0.147 MPa,采出程度为49.02%,提高幅度为5.19%。
综上所述,低、高密度颗粒由于重力分异作用,难以满足封堵需求,而等密度颗粒可通过注入水携带运移到所需封堵位置。
3 实际应用效果通过井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验可知,采用等密度、混合粒径的橡胶颗粒,当总用量越大,注水速度越大时,同时封堵横向底部通道和横向中部通道可以达到更好的驱油效果。
塔河油田TH25X井位于岩溶发育区,物质基础较好,储集体以裂缝-孔洞、溶洞型为主,完钻井深5 563.0 m,完钻层位为O2yj,钻井过程中在5 327.5~5 436.0 m井段漏失,于2013年8月27日常规投入生产,自喷期累产液0.94×104 t,累产油0.93×104 t,累产水85 t,初期不产水,见水后含水率快速上升至95%,截至2019年11月23日,该井累产油7.9×104 t,累产油4.1×104 t,累产水3.8×104 t。
2020年4月8日对该井进行橡胶颗粒调流实验,采用定位封堵和段塞式工艺进行调流,设置前置段塞橡胶颗粒粒径为2~4 mm,后置段塞橡胶颗粒粒径小于1 mm,橡胶颗粒和水同时注入,注入速度为50 m3/d,注入井筒总液量为920 m3,打压测试堵水成功。恢复生产后,截至2021年6月12日,累增油1 200 t,含水率下降15%,取得了较好的应用效果。
4 结论(1)井间单套缝洞型油藏橡胶颗粒调剖堵水模拟实验中,油水两相流动时固体介质对流体流动的阻力几乎为零,由于重力分异作用,注入水会沿着最低阻力方向流动,导致纵向波及系数较低;剩余油主要类型为阁楼油和绕流油,其分布受裂缝与溶洞空间位置的匹配关系影响;最终水驱含水率为98%时,采出程度为43.83%。
(2)在井间单套缝洞型油藏模拟实验中,同时封堵横向底部通道和横向中部通道驱油效果更好;橡胶颗粒可在高渗大孔缝中形成有效的架桥、堆积,迫使后续注入水转向低渗小孔缝,从而提高采出程度,采用混合粒径调流效果更好;颗粒的用量越大,封堵效果越好;与地层水等密度的橡胶颗粒可通过注入水携带运移到所需封堵位置,取得更好的封堵效果;注入调流剂的速度越大,水体携带原油能力越强,洗油效率越高,驱替效果越好。
(3)在塔河油田TH25X井现场试验中采用橡胶颗粒调流剂进行封堵,前置段塞橡胶颗粒粒径为2~4 mm,后置段塞橡胶颗粒粒径小于1 mm,颗粒密度为1.13 g/cm3,注水速度为50 m3/d,随水注入颗粒,总液量为920 m3,封堵后累增油1 200 t,含水率下降15%,应用效果较好。
| [1] |
李阳, 侯加根, 李永强. 碳酸盐岩缝洞型储集体特征及分类分级地质建模. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 600-606. LI Yang, HOU Jiagen, LI Yongqiang. Features and hierarchical modeling of carbonate fracture-cavity reservoirs. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 600-606. |
| [2] |
毛志强, 张雯, 吴春洲, 等. 纵向双层缝洞油藏橡胶颗粒调流适应性. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(5): 172-180. MAO Zhiqiang, ZHANG Wen, WU Chunzhou, et al. Flow regulation adaptability of rubber particles in longitudinal double-layer fractured-vuggy reservoirs. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(5): 172-180. |
| [3] |
宋传真, 马翠玉. 塔河油田奥陶系缝洞型油藏油水流动规律. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(4): 150-158. SONG Chuanzhen, MA Cuiyu. Oil-water flow law of Ordovician fractured-vuggy reservoirs in Tahe Oilfield. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(4): 150-158. |
| [4] |
杨祖国, 艾克热木·牙生, 高秋英, 等. 高矿化度缝洞型油藏用棉籽油-硫磺基密度可调颗粒调流剂的研发. 油田化学, 2020, 37(2): 212-217. YANG Zuguo, YASHENG Aikeremu, GAO Qiuying, et al. The cottonseed oil/sulfur based density adjustable particle agent applied in high salinity fractured-vuggy reservoir for fluid diversion. Oilfield Chemistry, 2020, 37(2): 212-217. |
| [5] |
杨美华, 钟海全, 李颖川. 缝洞型碳酸盐岩油藏新型油藏生产指示曲线. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(2): 163-170. YANG Meihua, ZHONG Haiquan, LI Yingchuan. New production index curve of fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(2): 163-170. |
| [6] |
葛丽珍, 孟智强, 朱志强, 等. 气顶边水油藏初期合理采油速度三维物理模拟实验. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(6): 99-105. GE Lizhen, MENG Zhiqiang, ZHU Zhiqiang, et al. Three-dimensional physical simulation experiment of reasonable initial oil recovery rate for the gas cap/edge water reservoirs. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(6): 99-105. |
| [7] |
张继春, 张津海, 杨延辉, 等. 潜山裂缝油藏降压开采增油机理及现场试验. 石油学报, 2004, 25(1): 52-56. ZHANG Jichun, ZHANG Jinhai, YANG Yanhui, et al. Mechanism of depressurization development of fractured reservoirs for enhancing oil production and in situ experiment. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(1): 52-56. |
| [8] |
CHEN Xin, LI Yiqiang, LIU Zheyu, et al. Investigation on matching relationship and plugging mechanism of self-adaptive microgel(SMG)as a profile control and oil displacement agent. Powder Technology, 2020, 364: 774-784. |
| [9] |
YANG Hongbing, ZHOU Bobo, ZHU Tongyu, et al. Conformance control mechanism of low elastic polymer microspheres in porous medium. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 196: 107708. |
| [10] |
王敏, 赵国良, 孙天建, 等. 分汊与游荡型辫状河隔夹层层次结构特征. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 39(6): 69-77. WANG Min, ZHAO Guoliang, SUN Tianjian, et al. Hierarchy characterization of intercalations in branching-based and wandering-based braded river reservoirs. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science and Technology Edition), 2017, 39(6): 69-77. |
| [11] |
LIN Meiqin, ZHANG Guiqing, HUA Zhao, et al. Conformation and plugging properties of crosslinked polymer microspheres for profile control. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2015, 477: 49-54. |
| [12] |
任文博. 流势调控在缝洞型碳酸盐岩油藏控水稳油中的应用. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(6): 127-134. REN Wenbo. Application of flow potential control in water control and oil stabilization of fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(6): 127-134. |
| [13] |
王成文, 王瑞和, 程荣超, 等. 溶洞-裂缝型复杂井堵漏新型触变水泥体系研究. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(5): 48-50. WANG Chengwen, WANG Ruihe, CHENG Rongchao, et al. Investigation on new thixotropic cement system for lost circulation control in vug-fracture type complex wells. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2007, 31(5): 48-50. |
| [14] |
YUAN Chengdong, PU Wanfen, JIN Fayang, et al. Performance of oil-based cement slurry as a selective water-plugging agent in high-temperature and high-salinity cave-fractured carbonate reservoirs. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(14): 6137-6149. |
| [15] |
车洪昌, 任耀宇, 刘汉平, 等. 龙虎泡油田活性水驱油室内实验研究. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(2): 128-132. CHE Hongchang, REN Yaoyu, LIU Hanping, et al. Laboratory study on oil displacement with active water in Longhupao Oilfield. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(2): 128-132. |
| [16] |
DU Guangyan, PENG Yuanyuan, PEI Yuxin, et al. Thermo-responsive temporary plugging agent based on multiple phase transition supramolecular gel. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(9): 9283-9289. |
| [17] |
ZHANG Yi, CAI Hongyan, LI Jiangguo, et al. Experimental study of acrylamide monomer polymer gel for water plugging in low temperature and high salinity reservoir. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 2018, 40(24): 1-12. |
| [18] |
曹伟佳, 卢祥国, 张云宝, 等. 淀粉接枝共聚物凝胶堵水效果及作用机理研究. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(1): 44-50. CAO Weijia, LU Xiangguo, ZHANG Yunbao, et al. Study on water plugging effect and mechanism of starch graft copolymer gel. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2019, 9(1): 44-50. |
| [19] |
吴刚, 余吉良, 林岳华, 等. 高温凝胶深部调剖剂的研究及在华北油田西柳10断块的应用. 石油钻采工艺, 2012, 34(1): 100-102. WU Gang, YU Jiliang, LIN Yuehua, et al. Research and uses of high-temperature gel deep modified profile agent in Fault 10 Xiliu Huabei Oilfield. Oil Drilling and Production Technology, 2012, 34(1): 100-102. |
| [20] |
赵光, 戴彩丽, 由庆. 冻胶分散体软体非均相复合驱油体系特征及驱替机理. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(3): 464-473. ZHAO Guang, DAI Caili, YOU Qing. Characteristics and displacement mechanisms of the dispersed particle gel soft heterogeneous compound flooding system. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(3): 464-473. |
| [21] |
徐婷, 李秀生, 张学洪, 等. 聚合物驱后提高原油采收率平行管试验研究. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(6): 98-100. XU Ting, LI Xiusheng, ZHANG Xuehong, et al. Parallel-column experiments for enhancing oil recovery after Polymer flooding. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(6): 98-100. |
 2023, Vol. 35
2023, Vol. 35